The NLRP3 inflammasome consists of NLRP3, ASC and pro-caspase 1 proteins. With NLRP3 activation, pro-caspase 1 converts into caspase 1, which leads to release proinflammatory cytokines like IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-18 and TNF-α.
GSDMD = Gasdermin D, is a protein that plays a crucial role in the process of pyroptosis, a form of programmed cell death that occurs in response to infection or cellular stress.
NOTE: Both, inorganic and organic fluoride compounds, may affect NLRP3 expression by interfering with thyroid-hormone-regulated pathways.
Zhang Q, Li T, Shi R, Qi R, Hao X, Ma B - "Fluoride promotes the secretion of inflammatory factors in microglia through NLRP3/Caspase-1/GSDMD pathway" Environ Sci Pollut Res Int (2024) doi: 10.1007/s11356-024-32443-6
https://link.springer.com/article/10.10 ... 24-32443-6
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38367109/
Abstract
It is widespread of endemic fluorosis in China, and the exposure of excessive fluoride will cause nervous system disease and activate microglia. However, the mechanism of the damage is not clear. It is well-known that NLRP3/Caspase-1/GSDMD pathway, a classic pyroptosis pathway, is widely involved in the occurrence and development of nervous system-related diseases, infectious diseases, and atherosclerotic diseases. This research aimed to explore the molecular mechanism of sodium fluoride on inflammation and pyroptosis in BV2 microglia based on the NLRP3/Caspase-1/GSDMD signaling pathway. BV2 microglia was treated with sodium fluoride at the dose of 0.25, 1, and 2 mmol/L for 24, 48, and 72 h, respectively. Cell viability, cell morphology, lactate dehydrogenase content, and related proteins and genes were examined to investigate if sodium fluoride caused damage to BV2 microglia through the pyroptosis pathway. Dithiolam (5 μmol/L), a pyroptosis inhibitor, was added for further verification. NaF could induced BV2 cells injury in a dose-dependent fashion through disrupting the integrity of cell membranes and increasing IL-1β via upregulating NLRP3, Caspase-1, and its downstream protein GSDMD. Disulfiram could improve these changes caused by NaF. In conclusion, our results suggested that NLRP3/Caspase-1/GSDMD-mediated classical pyroptosis pathway was involved in fluoride-induced BV2 microglia damage.
NLRP3 and Thyroid Hormone
Dong X, Yang H, Li C, Liu Q, Bai Q, Zhang Z - "Triiodothyronine alleviates alcoholic liver disease injury through the negative regulation of the NLRP3 signaling pathway" Exp Ther Med 16(3):1866-1872 (2018). doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.6409
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6122124/
"T3 negatively regulates the NLRP3-Caspase-1-pro-IL-1β-IL-1β signaling pathway and the NLRP3-TGF-β1 signaling pathway."
Głombik K, Detka J, Budziszewska B - "Venlafaxine and L-Thyroxine Treatment Combination: Impact on Metabolic and Synaptic Plasticity Changes in an Animal Model of Coexisting Depression and Hypothyroidism" Cells 10(6):1394 (2021). doi: 10.3390/cells10061394
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34198731/
"...an unfavorable change caused by the lack of thyroid hormones was an increase in the caspase-1 level..."
Ma B, Chen D, Liu Y, Zhao Z, Wang J, Zhou G, Xu K, Zhu T, Wang Q, Ma C -"Yanghe Decoction Suppresses the Experimental Autoimmune Thyroiditis in Rats by Improving NLRP3 Inflammasome and Immune Dysregulation" Front Pharmaco 12:645354 (2021). doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.645354
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34234669/
Sahin E, Bektur E, Baycu C, Burukoglu Dönmez D, Kaygısız B - "Hypothyroidism Increases Expression of Sterile Inflammation Proteins in Rat Heart Tissue" Acta Endocrinol (Buchar) 5(1):39-45 (2019). doi: 10.4183/aeb.2019.39
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6535312/
Sun YJ, Zhang YF, Xu HM, Ma YT, Li C, Nie CH, Zhao M - "Morin Improves Experimental Autoimmune Thyroiditis in Rats via NLRP3/Caspase-1 Pathway" Sichuan University. Medical Science Edition 52(2):229-234 (2021). Chinese. doi: 10.12182/20210160507
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33829696/
Vargas R, Videla LA - ". Thyroid hormone suppresses ischemia-reperfusion-induced liver NLRP3 inflammasome activation: Role of AMP-activated protein kinase" Immunol Lett 184:92-97(2017). doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2017.01.007
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/a ... 7816302747
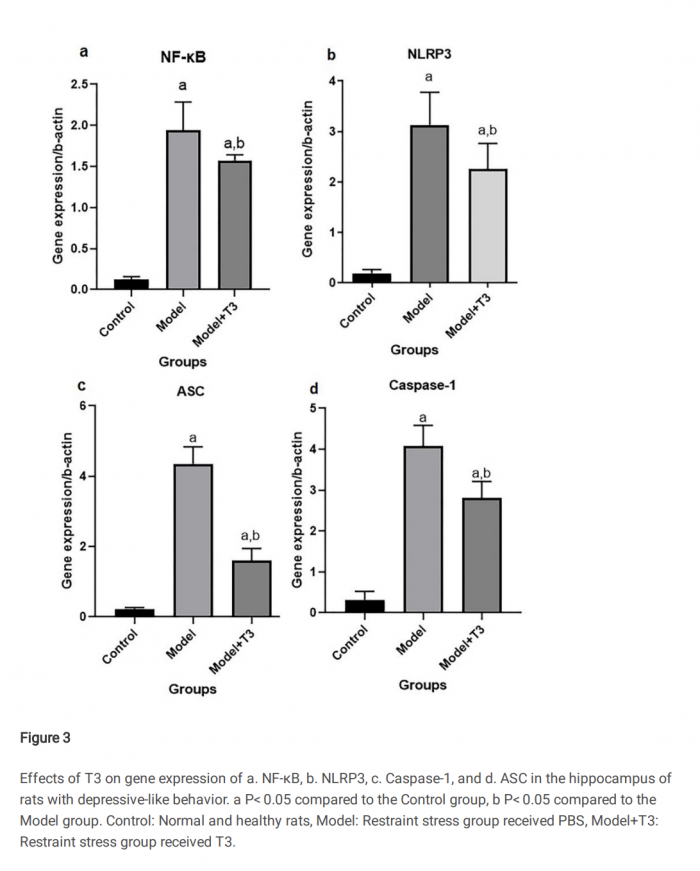
Tahmineh Mokhtari, AymanEl-Meghawry El-Kenawy, Li Hu - "Intraventricular T3 reverses chronic restraint stress-induced depressive-like behaviors: Inhibition of NF-κB/NLRP3 inflammasome pathway in the hippocampus" (2021)
https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-226593/v1
PFAS
Wang LQ, Liu T, Yang S, Sun L, Zhao ZY, Li LY, She YC, Zheng YY, Ye XY, Bao Q, Dong GH, Li CW, Cui J - "Perfluoroalkyl substance pollutants activate the innate immune system through the AIM2 inflammasome" Nat Commun 12(1):2915 (2021). doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-23201-0
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8131593/
"Mechanistically, PFOS activates the AIM2 inflammasome in a process involving mitochondrial DNA release through the Ca2+-PKC-NF-κB/JNK-BAX/BAK axis..." Here PFOS induced caspase-1 activation - but not through NLRP3, but AIM2. In liver PFOS acts via NLRP3 (see Qin 2022, below).
Shi B, Zhang Z, Xing J, Liu Q, Cai J, Zhang Z - "Perfluorooctane sulfonate causes pyroptosis and lipid metabolism disorders through ROS-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation in grass carp hepatocyte" Aquat Toxicol 267:106839 (2024). doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2024.106839
https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retriev ... 24)00010-9
"This research demonstrated that PFOS drives NLRP3 inflammasome activation through oxidative stress induced by reactive oxygen species overload. This in turn leads to pyroptosis and lipid metabolism disorders." NOTE: ROS --> Gq/11
Wang T, Xu H, Guo Y, Guo Y, Guan H, Wang D - "Perfluorodecanoic acid promotes high-fat diet-triggered adiposity and hepatic lipid accumulation by modulating the NLRP3/caspase-1 pathway in male C57BL/6J mice" Food Chem Toxicol 178:113943 (2023). doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2023.113943
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/a ... 1523003459
"PFDA may enhance HFD-induced adiposity and hepatic lipid accumulation through the NLRP3/caspase-1 pathway. This contaminant may be a key risk factor for obesity development in individuals consuming high-fat foods, particularly Western diet."
Qin Y, Gu T, Ling J, Luo J, Zhao J, Hu B, Hua L, Wan C, Jiang S - "PFOS facilitates liver inflammation and steatosis: An involvement of NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated hepatocyte pyroptosis" J Appl Toxicol 42(5):806-817 (2022). doi: 10.1002/jat.4258
https://analyticalsciencejournals.onlin ... 2/jat.4258
Resveratrol
Bartra C, Yuan Y, Vuraić K, Valdés-Quiroz H, Garcia-Baucells P, Slevin M, Pastorello Y, Suñol C, Sanfeliu C - "Resveratrol Activates Antioxidant Protective Mechanisms in Cellular Models of Alzheimer's Disease Inflammation" Antioxidants (Basel) 13(2):177 (2024. doi: 10.3390/antiox13020177.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10886200/
Gq/11
Xu M, Jiang Z, Wang C, Li N, Bo L, Zha Y, Bian J, Zhang Y, Deng X - "Acetate attenuates inflammasome activation through GPR43-mediated Ca2+-dependent NLRP3 ubiquitination" Exp Mol Med 51(7):1-13 (2019). doi: 10.1038/s12276-019-0276-5
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6802670/
"Here, we demonstrate that acetate attenuates inflammasome activation via GPR43 in a Ca2+-dependent manner. Through binding to GPR43, acetate activates the Gq/11 subunit and subsequent phospholipase C-IP3 signaling to decrease Ca2+ mobilization...Collectively, our research demonstrates that acetate regulates the NLRP3 inflammasome via GPR43 and Ca2+-dependent mechanisms, which reveals the mechanism of metabolite-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome attenuation and highlights acetate as a possible therapeutic strategy for NLRP3 inflammasome-related diseases."